
The biopharmaceutical industry operates under strict regulations, and effective supply chain management is crucial for patient safety and timely access to treatments. The biopharmaceutical supply chain is responsible for ensuring efficient and secure delivery of drugs and vaccines while maintaining product quality. Challenges such as compliance, risk management, and technology adoption have emerged in recent years. Cold chain management, monitoring technologies, and new regulations like DSCSA and FMD have impacted the industry. Adhering to trends and regulations, including blockchain and artificial intelligence, can improve transparency, traceability, and efficiency in supply chain management, ultimately ensuring the safe and prompt delivery of life-saving treatments to patients.

The biopharmaceutical industry is a highly regulated and complex industry, where the timely and safe delivery of life-saving treatments to patients is of utmost importance. To ensure patient safety and product quality, the industry must adhere to strict regulations and guidelines governing the manufacturing, distribution, and supply of biopharmaceutical products. In recent years, there have been several trends and regulatory changes that have impacted the bio-pharmaceutical supply chain. This article provides an overview of these trends and regulations and their implications for bio-pharmaceutical supply chain management.
Bio-Pharmaceutical Supply Chain New Regulations and Challenges and Trends
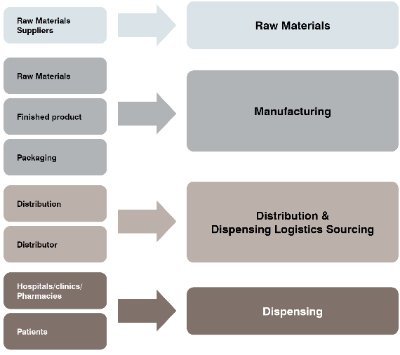
The Bio-Pharmaceutical Supply Chain involves a complex network of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and regulatory bodies. This complexity can create challenges in managing the supply chain and ensuring the quality of the final product. Hence, Bio Pharmaceutical Supply Chain is subject to a range of challenges, including those related to regulatory compliance, quality control, supply chain visibility, and risk management. However, by implementing effective strategies and technologies, companies can overcome these challenges and ensure the safe and timely delivery of life-saving medications to patients around the world. Examples of such strategies and technologies include quality control measures, real-time monitoring systems, risk management strategies, and collaborative planning processes. By prioritizing effective supply chain management, bio-pharmaceutical companies can continue to fulfill their mission of improving human health and well-being.
In recent years, there have been several new regulations introduced that impact the biopharmaceutical supply chain. One of the most significant regulatory changes is the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) in the United States. The DSCSA is designed to enhance the security and traceability of pharmaceutical products by requiring the use of unique product identifiers and serialization. Under the DSCSA, all pharmaceutical products must have a unique product identifier, which enables traceability of the product throughout the supply chain. This includes the ability to track the product from the manufacturer to the dispenser and to verify the authenticity of the product at each stage of the supply chain.
Another regulatory change that impacts the bio-pharmaceutical supply chain is the Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) in the European Union. The FMD is designed to prevent the entry of falsified medicines into the supply chain by requiring the use of serialization and track-and-trace technologies. Under the FMD, all prescription medicines must have a unique identifier, which enables traceability of the product throughout the supply chain.
This includes the ability to track the product from the manufacturer to the patient and to verify the authenticity of the product at each stage of the supply chain.

To comply with the DSCSA, companies must implement serialization and track-and-trace technologies that enable them to capture and exchange data about drug products throughout the supply chain. This includes investing in systems for printing and verifying unique identifiers, as well as software solutions for managing serialization data and communicating with supply chain partners.
Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) - European Union the FMD requires that all prescription drug products in the European Union be serialized and tracked through the supply chain using a unique identifier by February 9, 2019. The Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD) is aimed at preventing the entry of falsified medicines into the supply chain. The law requires pharmaceutical companies to place a unique identifier on the packaging of prescription drugs, which can be scanned at various points in the supply chain to verify the authenticity of the product. The law also requires the use of tamper-evident packaging and the reporting of suspect products. This information must be maintained for at least five years and be readily retrievable upon request by the authorities.
Both the DSCSA and the FMD have had a significant impact on the bio-pharmaceutical supply chain, requiring companies to invest in new technology and processes to comply with the law. While the regulations have increased the security and safety of the supply chain, they have also increased the cost and complexity of doing business. As a result, companies are looking for new ways to streamline their supply chain processes and reduce costs, such as using automation and digitalization.
Bio-Pharmaceutical Supply Chain also faces several other challenges. One of the biggest challenges is ensuring product integrity throughout the supply chain. Recently, there has been a growing trend of outsourcing, and the need for effective technology adoption. By staying up-to-date with the latest trends and regulations, and by implementing effective supply chain strategies and technologies, biopharmaceutical companies can ensure the safe and timely delivery of life-saving treatments to patients around the world, while also improving supply chain efficiency and reducing costs.
Regulatory Compliance:
The Bio-Pharmaceutical Supply Chain is subject to a wide range of regulatory requirements, including those related to product safety, quality, and efficacy. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in ignificant financial and reputational damage.
An example of this challenge is the need to comply with strict transportation and storage requirements for temperature-sensitive products, such as vaccines and biologics. These products require precise temperature control throughout the supply chain to maintain their efficacy and safety.
Quality Control:
The bio-pharmaceutical supply chain should ensure the quality of raw materials used in the manufacturing process. Poor quality materials can lead to quality issues in the final product, resulting in regulatory sanctions, product recalls, and harm to patients.
Supply Chain Visibility:
The Bio-Pharmaceutical Supply Chain requires visibility and transparency throughout the supply chain to ensure the timely delivery of products, minimize the risk of stockouts, and optimize inventory levels. However, achieving this visibility can be challenging due to the complex nature of the supply chain and the need to protect patient privacy.
Risk Management:
The Bio-Pharmaceutical Supply Chain is subject to a wide range of risks, including those related to supplier quality, transportation, and regulatory compliance.
Effective risk management is essential to ensure the continuity of the supply chain and prevent disruptions.
Using temperature-controlled packaging and transportation:
To maintain the required temperature range during shipping. These packages are designed to maintain a specific temperature range for a set period, often using insulated materials and gel packs or dry ice. In addition to packaging, many companies also use temperature monitoring technologies, such as data loggers or real-time monitoring systems, to ensure that products are kept within the required temperature range throughout the supply chain.
The risk of counterfeiting and product diversion:
Counterfeit drugs can pose serious health risks to patients and undermine public trust in the pharmaceutical industry. To address this challenge, many companies use to track and trace technologies, such as serial numbers or barcodes, to monitor the movement of products through the supply chain and verify their authenticity. To further improve supply chain security, some companies are also exploring the use of blockchain technology. Blockchain can provide a secure and transparent record of the movement of products through the supply chain, making it easier to detect and prevent counterfeiting and diversion.
By prioritizing supply chain management and implementing best practices and technologies, biopharmaceutical companies can ensure the safe and timely delivery of life-saving treatments to patients around the world.
Looking to the future, the bio-pharmaceutical supply chain will continue to evolve, with new technologies and regulations shaping the industry. For example, the adoption of new gene and cell therapies may require new supply chain strategies and technologies to ensure their safe and effective delivery. Similarly, the growing focus on sustainability may require biopharmaceutical companies to develop more environmentally-friendly supply chain processes.
The use of temperature-controlled packaging and transportation, along with monitoring technologies, is crucial to ensuring the integrity of temperature-sensitive products in the bio-pharmaceutical supply chain. These technologies help to ensure that temperature-sensitive medications are transported and stored within the desired temperature range, thus maintaining their efficacy and safety and monitoring temperature conditions to identify potential issues before they result in product spoilage.
In conclusion, the use of temperature-controlled packaging and transportation, along with monitoring technologies, is essential to ensuring product integrity in the bio-pharmaceutical supply chain.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend of outsourcing in the industry, as companies seek to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and focus on their core competencies. This trend has significant implications for supply chain management, as outsourcing can impact the entire supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to customers.
Outsourcing can offer several benefits to biopharmaceutical companies, including cost savings, access to specialized expertise, and increased flexibility. However, outsourcing also poses several challenges to supply chain management, including the need for effective supplier management and risk mitigation strategies.
To mitigate these risks, biopharmaceutical companies must establish robust supplier qualification and selection processes, as well as implement effective supplier performance monitoring and risk management strategies.
Quality control: When outsourcing manufacturing or other supply chain activities, it can be difficult to maintain consistent quality across different vendors. This can be particularly challenging when working with vendors located in different countries with different regulatory environments and quality standards.
Intellectual property protection:
Outsourcing can increase the risk of intellectual property theft or infringement. Companies need to ensure that they have strong contracts and non-disclosure agreements in place with their vendors to protect their valuable intellectual property.
Regulatory compliance:
Companies need to ensure that their vendors are compliant with all relevant regulations, particularly in the areas of manufacturing and distribution. Failure to comply with regulations can result in significant fines or even product recalls.
To overcome these challenges, companies need to develop robust supply chain management strategies that consider the specific risks and challenges of outsourcing.
The bio-pharmaceutical supply chain is a complex network that involves multiple stakeholders, including manufacturers, distributors, wholesalers, pharmacies, and healthcare providers.
Blockchain is one technology that has gained significant attention. It is a distributed ledger technology that enables secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record-keeping. In the bio-pharmaceutical supply chain, blockchain can be used to improve transparency and traceability by enabling the secure sharing of data among supply chain partners. For example, blockchain can be used to track and record the movement of pharmaceutical products from the manufacturer to the patient, providing a secure and auditable record of the product's journey.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is another technology that has gained attention in bio-pharmaceutical supply chain management. AI can be used to improve supply chain efficiency and decision-making by analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying patterns and trends. For example, AI can be used to optimize inventory levels, predict demand, and identify supply chain bottlenecks.
However, the implementation of new technologies such as blockchain and AI can also pose challenges to supply chain management. For example, the integration of new technologies with existing systems and processes can be complex and may require significant investments in IT infrastructure and personnel training.
Another technology that can play a role in bio pharmaceutical supply chain management is artificial intelligence (AI). AI can be used to analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns and insights that can help to improve supply chain efficiency and reduce the risk of disruptions. For example, AI can be used to monitor inventory levels, predict demand, and optimize logistics routes. By providing real-time insights, AI can help to improve the responsiveness of the supply chain and reduce the risk of stockouts and delays.
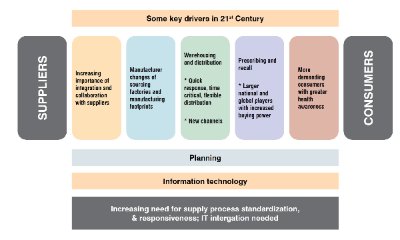
While blockchain and AI have the potential to improve the bio pharmaceutical supply chain, there are also challenges and limitations that must be considered. One of the main challenges is the need for interoperability and standardization across different stakeholders in the supply chain. For blockchain to be effective, all parties must be able to access and contribute to the shared ledger. This requires the development of common standards and protocols, which can be difficult to achieve in a highly regulated industry.
In terms of regulation, there are currently no specific regulations governing the use of blockchain and AI in the bio-pharmaceutical supply chain. However, companies must comply with existing regulations governing data privacy, security, and quality assurance. For example, companies must ensure that their blockchain platforms are compliant with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, which mandates strict rules for the collection, use, and storage of personal data. Similarly, companies must comply with the FDA's current good manufacturing practice (cGMP) regulations, which require that drugs be manufactured in accordance with strict quality standards.
For example, a biopharmaceutical company could use predictive analytics to analyze data on supplier performance, shipping times, and other relevant factors to identify potential delays or issues that could impact the supply chain. This information could then be used to take proactive measures to prevent or mitigate any potential disruptions.
In addition to AI, blockchain technology is also being explored as a potential solution for supply chain management in the biopharmaceutical industry. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that allows for secure, transparent, and immutable record-keeping. This can be particularly useful in the biopharmaceutical supply chain, where traceability and authenticity of products are critical.
Overall, the use of technology in biopharmaceutical supply chain management is becoming increasingly important as the industry continues to grow and evolve. By leveraging AI, blockchain, and other advanced technologies, biopharmaceutical companies can improve efficiency, transparency, and traceability in their supply chains, leading to better patient outcomes.
The importance of staying up-to-date with the latest trends and regulations in bio-pharmaceutical supply chain management, to ensure the safe and timely delivery of life-saving treatments to patients.
Staying up-to-date with the latest trends and regulations in bio pharmaceutical supply chain management is crucial for ensuring the safe and timely delivery of life-saving treatments to patients. The rapidly evolving nature of the industry means that new challenges and opportunities are constantly emerging, and those who can adapt quickly are more likely to succeed.
Effective supply chain management requires a deep understanding of both the regulatory environment and the latest technological advancements. As we have seen, new regulations such as the DSCSA and FMD have created a need for greater transparency and traceability in the supply chain and have led to the adoption of new serialization and track-and-trace technologies. In addition, the growing trend of outsourcing has made it increasingly important to have robust supplier management and risk mitigation strategies in place.
Staying up-to-date with the latest trends and regulations requires ongoing education and training, as well as a willingness to embrace new technologies and approaches. Companies that prioritize these areas are more likely to remain competitive and successful in the rapidly evolving bio-pharmaceutical industry.
In conclusion, the bio-pharmaceutical supply chain is a complex and rapidly evolving ecosystem, with numerous challenges and opportunities for those involved. Bio-Pharmaceutical Companies must stay up-to-date with the latest trends and regulations in supply chain management and implement effective supply chain strategies and technologies. This includes the establishment of robust cold chain management processes, the implementation of serialization and track-and-trace technologies, effective supplier management and risk mitigation strategies, and the integration of recent technologies such as block chain and AI. Staying up-to-date with the latest trends and regulations, and leveraging the latest technological advancements, is crucial for ensuring the safe and timely delivery of life-saving treatments to patients around the world.
References: